Pipeline
Getting Started¶
The GitHub CI/CD pipeline includes the following steps.
The pipelines uses environment secrets (under the defined environment 'dev', 'staging' and 'production') for code coverage and for the role to deploy to AWS.
When you clone this repository be sure to define the environments in your repo settings and create a secret per environment:
- AWS_ROLE - to role to assume for your GitHub worker as defined here
Makefile Commands¶
All steps can be run locally using the makefile. See details below:
- Create Python environment
- Install dev dependencies
- Run pre-commit checks as defined in
.pre-commit-config.yaml - Lint and format and sort imports with ruff (similar to flake8/yapf/isort) - run
make formatin the IDE - Static type check with mypy as defined in
.mypy.ini- runmake lintin the IDE - Verify that Python imports are sorted according to standard - run
make sortin the IDE - Python complexity checks: radon and xenon - run
make complexin the IDE - Unit tests. Run
make unitto run unit tests in the IDE - Infrastructure test. Run
make infra-teststo run the CDK infrastructure tests in the IDE - Code coverage by codecov.io
- Deploy CDK - run
make deployin the IDE, will also run security tests based on cdk_nag - Integration tests - run
make integrationin the IDE. - E2E tests - run
make e2ein the IDE - Code coverage tests - run
make coverage-testsin the IDE after CDK dep - OpenAPI Swagger file - run
- Update GitHub documentation branch
- Update dependencies and CDK version automatically to the latest versions: run
make update-deps.
Other Capabilities¶
- Automatic Python dependencies update with Dependabot
- Easy to use makefile allows to run locally all commands in the GitHub actions
- Run local docs server, prior to push in pipeline - run
make docsin the IDE - Prepare PR, run all checks with one command - run
make prin the IDE
Environments & Pipelines¶
All GitHub workflows are stored under .github/workflows folder.
The two most important ones are pr-serverless-service and main-serverless-service.
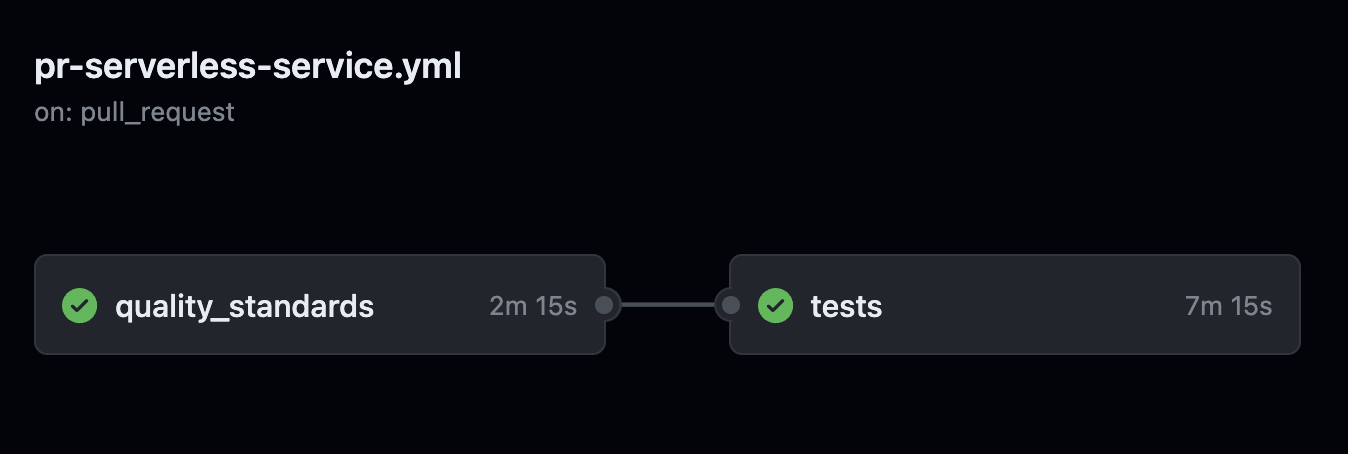
pr-serverless-service¶
pr-serverless-service runs for every pull request you open. It expects you defined a GitHub environments by the name dev, staging and production and for each environments to have the following variables: CODECOV_TOKEN for CodeCov integration and AWS_ROLE that allows GitHub to deploy to that AWS account (one for dev, one for staging and one for production accounts).
It includes two jobs: 'quality_standards' and 'tests' where a failure in 'quality_standards' does not trigger 'tests'. Both jobs MUST pass in order to to be able to merge.
'quality_standards' includes all linters, pre-commit checks and units tests and 'tests' deploys the service to AWS, runs code coverage checks,
checks that your OpenAPI file is up to date and corresponds to the actual deployment (fails if it does not, hence your documentation is out of date), security checks and E2E tests. Stack is destroyed at the end. Stack has a 'dev'
prefix as part of its name. Each environment has a pre-defined stack prefix.
Once merged, main-serverless-service will run.
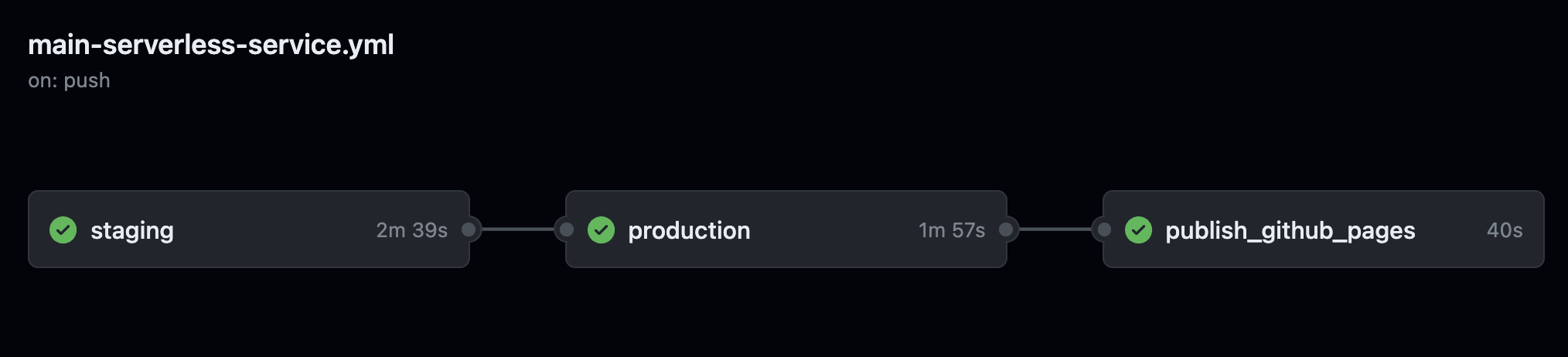
main-serverless-service¶
main-serverless-service runs for every MERGED pull request that runs on the main branch. It expects you defined a GitHub environments by the name staging and production and that both includes a secret by the name of AWS_ROLE.
It includes three jobs: 'staging', 'production' and 'publish_github_pages'.
'staging' does not run any of the 'quality_standards' checks, since they were already checked before the code was merged. It runs just coverage tests and E2E tests. Stack is not deleted. Stack has a 'staging' prefix as part of its name. Any failure in staging will stop the pipeline and production environment will not get updated with the new code.
'production' does not run any of the 'quality_standards' checks, since they were already checked before the code was merged. It does not run any test at the moment. Stack is not deleted. Stack has a 'production' prefix as part of its name.